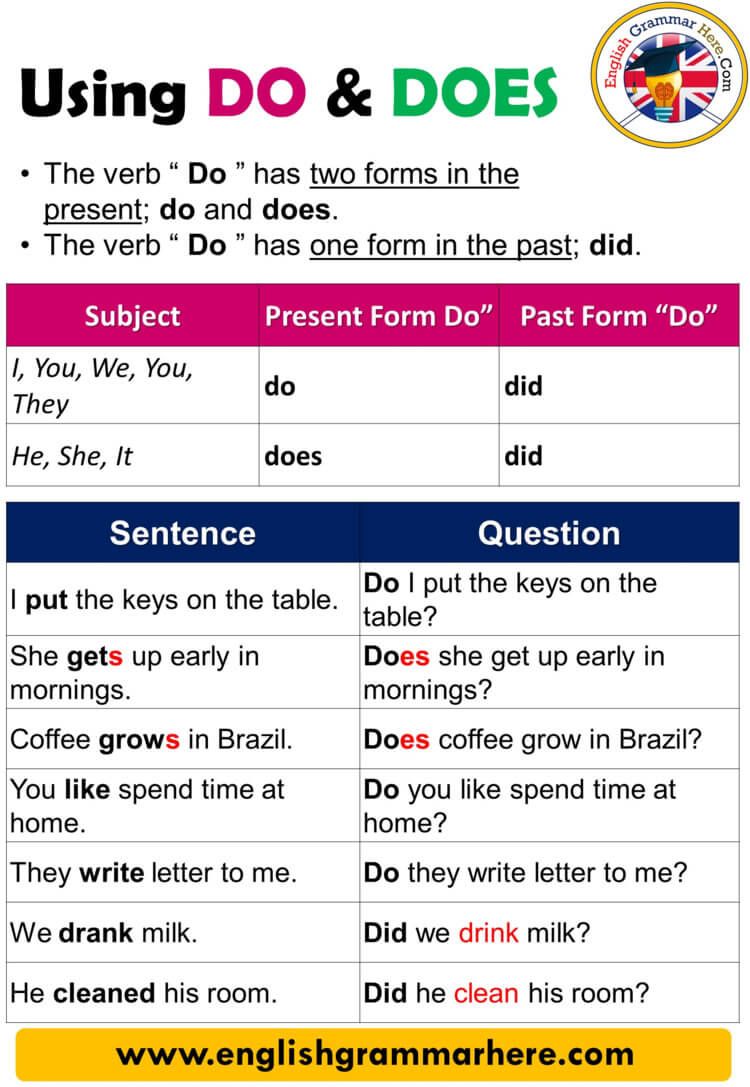
Mastering Modern Technology Sales: Strategies, Tools, and Actionable Steps for 2025
Introduction: Navigating the New Era of Technology Sales
Selling technology in 2025 demands a dynamic approach tailored to digitally empowered buyers, rapidly advancing tools, and ever-shifting market expectations. Success now hinges on combining advanced sales technology with human insight, personalized interactions, and agile strategies. This article provides a comprehensive roadmap-covering current trends, proven techniques, step-by-step processes, and solutions to common challenges-so you can confidently drive results in today’s competitive landscape.
Understanding the 2025 Technology Sales Landscape
The technology sales environment has evolved rapidly. Buyers today are informed, value-driven, and expect seamless, digital-first experiences. According to industry experts, 80% of B2B sales communication between suppliers and buyers will occur in digital channels by 2025 [3] . AI-driven platforms, digital self-service, and data-powered selling are now standard across leading sales organizations [1] . To thrive, sellers must adapt to these shifts by integrating technology, nurturing relationships, and delivering genuine value.
Key Trends Shaping Technology Sales
1. AI and Automation as Core Sales Drivers
Artificial intelligence (AI) isn’t just another tool-it is now central to sales operations. AI enables teams to prioritize leads, automate repetitive tasks like follow-ups and scheduling, and personalize outreach at scale [1] . For example, AI can analyze buyer behavior, recommend next steps, and even generate tailored emails in seconds. According to Gartner, 35% of chief revenue officers will establish centralized AI teams to drive sales effectiveness by 2025 [1] .
Implementation Steps:
- Research and select an AI-powered CRM or sales enablement platform with proven results (consider platforms with verified case studies).
- Train your team on leveraging AI features for lead scoring, next-best-action recommendations, and automated communications.
- Monitor AI-driven outcomes and refine strategies for continuous improvement.
Example: A technology reseller uses AI to analyze customer engagement data, prioritizing prospects likely to convert and automatically sending follow-up reminders to sales reps.
Potential Challenges: Over-reliance on automation can depersonalize interactions. Balance AI efficiency with authentic human touch.
2. Expanding Digital Touchpoints and Hybrid Selling
Buyers now expect to interact with sales teams across multiple digital channels-email, live chat, social media, and even SMS. Hybrid selling blends online and offline outreach, giving prospects flexibility and convenience. Studies show 90% of companies are willing to complete high-value deals entirely online [3] .
Actionable Guidance:

Source: alamy.com
- Audit your current sales process to identify gaps in digital availability (e.g., lack of live chat or social media presence).
- Invest in digital sales tools verified by industry leaders (such as video conferencing, chatbots, and e-signature platforms).
- Train sales reps on managing digital communication and online relationship-building.
Alternative Approaches: For markets less receptive to digital-only interactions, maintain a hybrid presence-offering both digital touchpoints and traditional meetings as needed.
3. Personalized, Data-Driven Outreach
Generic pitches are no longer effective. Buyers respond to personalized communication that demonstrates a clear understanding of their needs. Leveraging data analytics, sales teams can craft tailored messages and offers, increasing engagement and trust [5] .
Step-by-Step:
- Collect and segment customer data using a verified CRM platform.
- Develop buyer personas to guide messaging strategies.
- Craft custom communication templates for each segment and refine them based on response analytics.
- Test different personalization approaches and iterate for best results.
Example: A SaaS provider sends personalized demo invitations based on industry pain points gathered from prospect profiles, resulting in higher conversion rates.
Building a Strong Sales Pipeline
A robust pipeline is the foundation of any technology sales strategy. Innovative outreach, account-based marketing, and social selling are crucial for attracting and nurturing high-quality leads [5] .
Step-by-Step Guidance:
- Identify Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Use verified industry reports and CRM data to define your target market.
- Leverage Social Selling: Share relevant content, join industry groups, and engage with decision-makers on trusted platforms like LinkedIn.
- Implement Account-Based Marketing (ABM): Develop targeted campaigns for high-value accounts, using personalized outreach and relevant content.
- Measure and Optimize: Use built-in analytics from your CRM to track pipeline health, conversion rates, and campaign effectiveness.
Alternative Pathways: For companies without access to advanced CRM platforms, start with manual segmentation using spreadsheets and gradually migrate to digital tools as resources allow.
Consultative Selling and Relationship Building
Modern technology sales require a consultative approach-understanding client goals, providing tailored solutions, and becoming a trusted advisor [1] . This method fosters long-term relationships and drives repeat business.
How to Implement:
- Begin every interaction by asking open-ended questions about the client’s business challenges.
- Listen actively, document needs, and propose solutions that align with their objectives.
- Share real-world case studies and examples relevant to their industry.
- Follow up regularly with insights, updates, and support-not just sales pitches.
Example: A cloud services consultant hosts quarterly review sessions with clients to assess solution impact and identify new opportunities.
Challenge: Building trust takes time; consistent, value-driven communication is key.
Post-Purchase Engagement and Customer Success
Closing the sale is just the beginning. Ongoing customer success management ensures satisfaction, encourages renewals, and generates referrals. Technology vendors are increasingly investing in post-purchase engagement using digital tools and dedicated support teams [2] .
Practical Steps:
- Set up onboarding processes using automated email sequences and digital knowledge bases.
- Schedule regular check-ins through verified video conferencing platforms.
- Gather feedback via online surveys and adjust support strategies as needed.
- Encourage customers to share their experiences on third-party review sites and industry forums.
Alternative Approach: For limited resources, prioritize high-impact clients for personalized engagement while using self-service resources for others.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Technology Sales
Some obstacles-such as long decision cycles, complex buying committees, and rapid technological change-are unique to the technology sector. Overcoming these requires a mix of agility, education, and strategic patience.
Solutions:

Source: valueforward.com
- Educate all stakeholders by providing clear, jargon-free resources and verified case studies.
- Be transparent about implementation timelines and potential challenges.
- Stay updated on industry trends through trusted sources (such as trade associations and major analyst firms).
Example: A cybersecurity vendor holds webinars for both technical and non-technical buyers to demystify product features and build consensus.
Actionable Steps for Getting Started
- Audit your current sales processes and digital capabilities.
- Identify gaps in technology adoption and customer engagement.
- Research and select verified tools that align with your needs (consult industry rankings and reviews).
- Train your team on new platforms and personalized selling techniques.
- Develop a plan for ongoing measurement and continuous improvement.
For additional support, consider joining professional sales associations, attending industry conferences, or consulting with technology sales experts whose credentials can be verified through reputable business networks.
References
- [1] SuperOffice (2025). Sales Trends in 2025 – SuperOffice CRM.
- [2] Destination CRM (2025). The Top Sales Trends and Technologies for 2025.
- [3] U.S. Chamber of Commerce (2024). Sales Strategies to Leverage in 2025.
- [4] Spinify (2025). 10 Key Sales Enablement Trends for 2025.
- [5] InAccord (2025). Building a Strong Sales Pipeline for 2025.
MORE FROM oncecoupon.com