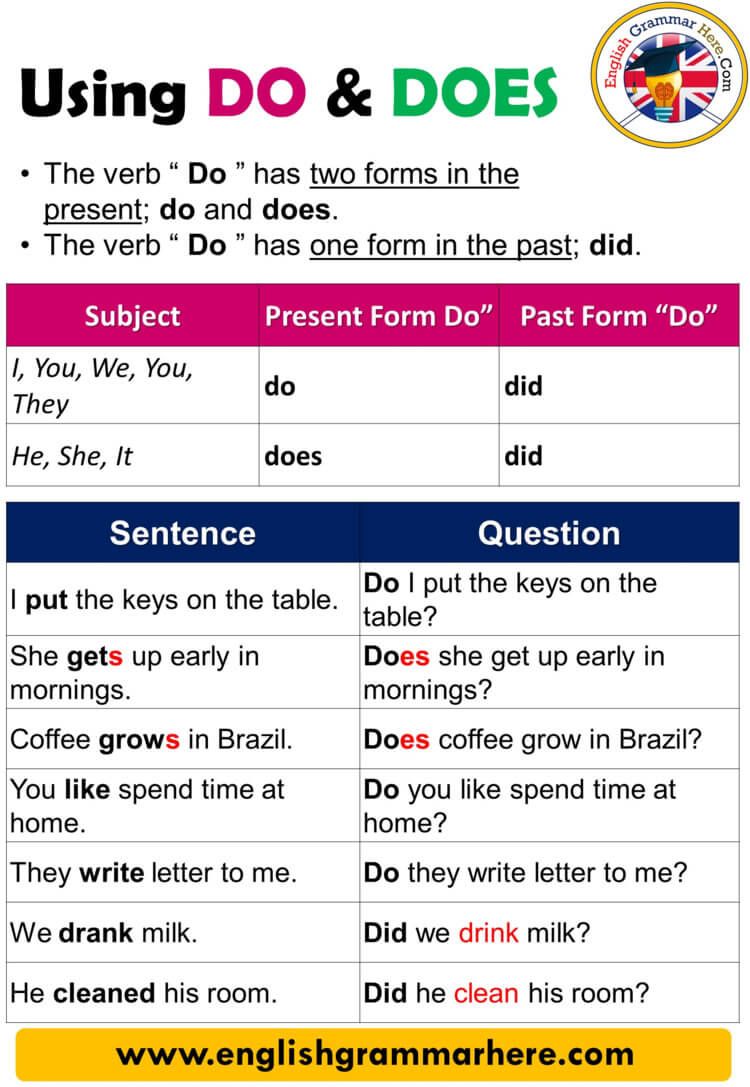
Step-by-Step Guide to Safely Removing a Conda Environment
Introduction to Conda Environment Removal
Managing Conda environments is essential for Python developers, data scientists, and machine learning practitioners. Over time, you may accumulate unused or outdated environments, which can clutter your workspace and consume disk space. Safely removing these environments not only streamlines your workflow but also helps prevent confusion and resource waste. This guide provides detailed, actionable steps for removing Conda environments using command-line tools, offers troubleshooting tips for common issues, and suggests alternative approaches for advanced scenarios. All guidance is based on verified documentation and real-world examples.
Understanding Conda Environments
A Conda environment is an isolated directory containing a specific Python interpreter and installed packages. These environments enable you to work on multiple projects with unique dependencies without causing conflicts. For example, you might have one environment for a TensorFlow project and another for Django development. Managing these environments efficiently is key to maintaining a clean and organized development setup [4] .

Source: blog.rteetech.com
Why Remove a Conda Environment?
There are several reasons to remove a Conda environment:
- You no longer need the environment for your project.
- The environment has become corrupted or is causing errors.
- You want to free up disk space.
- You need to reorganize or rename environments for better workflow management.
Removing unused environments helps maintain a tidy workspace and ensures your Conda installation runs smoothly.
Pre-Removal Checklist
Before you delete a Conda environment, consider these important points:
- Backup important data : If the environment contains valuable scripts, configuration files, or data, back them up before proceeding.
- Deactivate the environment : Conda does not allow removal of active environments, so ensure you are not currently using the one you want to delete.
-
List existing environments
: Use the command
conda env list
Step-by-Step Instructions for Removing a Conda Environment
Follow these steps to safely and effectively remove a Conda environment:
1. Open Your Conda Terminal
On Windows, launch the “Anaconda Powershell Prompt” by searching for it in your Start menu. On macOS or Linux, open your preferred terminal application.
2. List All Conda Environments
Run the following command to display all environments and their locations:
conda env listThis will help you identify the exact name of the environment you wish to remove.
3. Deactivate the Environment
If you are currently inside the environment, deactivate it by executing:
conda deactivateThis step is mandatory, as trying to remove an active environment will result in an error [3] .
4. Remove the Conda Environment
Now, delete the environment by running:
conda env remove --name <environment-name>
Replace
<environment-name>
conda env remove --name myenv
Upon successful removal, the environment will no longer appear in the list when you run
conda env list
Troubleshooting: Removing Corrupted or Stubborn Environments
Occasionally, a Conda environment may become corrupted and resist deletion via standard commands. In such cases, you can manually remove the environment as follows:
-
Locate your Conda installation directory. By default, environments reside in the
envs
-
Navigate to the
envs
-
After deletion, run
conda env list
Manual deletion should only be used when the standard command fails, as it does not clean up all metadata and may leave orphaned references.

Source: blog.rteetech.com
Alternative Removal Command
Some users prefer using an alternative command for removal:
conda remove --name <environment-name> --all
This command removes all packages from the specified environment and deletes it entirely. Both methods are effective, but
conda env remove
Best Practices for Environment Management
Effective environment management helps avoid clutter and confusion:
- Regularly audit environments : List and review environments to identify those no longer needed.
- Use descriptive names : When creating environments, choose clear and project-specific names to simplify identification.
-
Document dependencies
: Export environment specifications for future reference using
conda list --explicit > requirements.txt
- Consider renaming environments : Conda does not directly support renaming, but you can export packages from an old environment, create a new one, and install packages there [2] .
Case Study: Managing Multiple Projects
Imagine a developer who maintains separate Conda environments for data analysis, web development, and machine learning. Over time, some projects are completed or abandoned, leaving behind unused environments. By regularly listing environments and removing those no longer needed, the developer avoids clutter and potential confusion. This proactive approach also frees up disk space and reduces maintenance overhead.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While removing Conda environments is straightforward, some challenges may arise:
- Environment not deleted : If the environment persists after running the removal command, try manual deletion as described above.
- Permission errors : On some systems, you may require administrative privileges to delete environment directories. Use elevated permissions if necessary.
- Active environment warning : Always confirm you have deactivated the environment before attempting removal.
- Dependency leftovers : Manual deletion may leave package remnants. Consider running cleanup tools or reviewing environment folders periodically.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Removing a Conda environment is a vital part of maintaining a clean, efficient development workflow. The process involves listing environments, deactivating the target, and executing the removal command. For stubborn or corrupted environments, manual deletion may be necessary. By following best practices and regularly auditing your setups, you can ensure your workspace remains organized and efficient. If you encounter issues, consult the official Conda documentation or community forums for further guidance.
References
- [1] Metaschool (2024). How to Remove a Conda Environment? Step-by-step removal guide.
- [2] Kanaries Docs (2024). How to Remove Conda Environment: Best Practices & Commands.
- [3] Conda Documentation (2024). conda env remove – conda 25.7.0 documentation.
- [4] Conda Documentation (2019). Managing environments – conda 25.7.1.dev22 documentation.
- [5] Anaconda Forum (2023). Cmd to remove conda environment.
MORE FROM oncecoupon.com