Practicum in Education: Essential Field Experience for Future Educators
Understand practicum in education
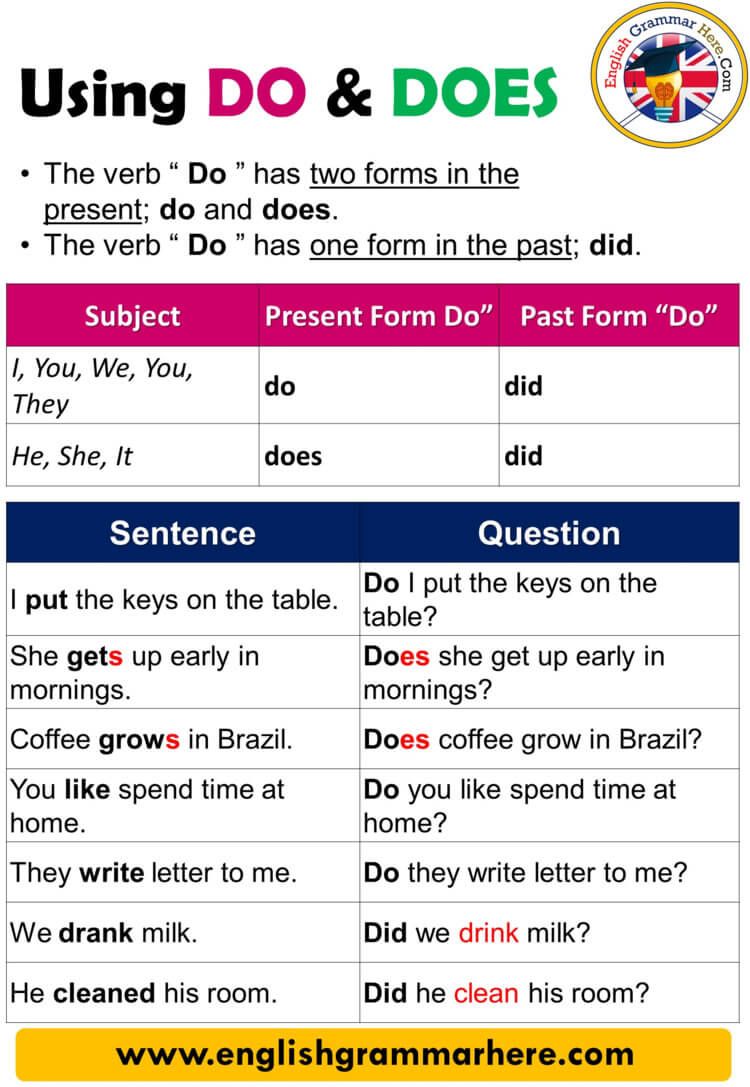
A practicum in education represent a supervised, hands-on learning experience where students apply theoretical knowledge in real educational settings. Unlike standard classroom learning, practicums immerse future educators in authentic teaching environments under the guidance of experienced mentors. This critical component of teacher preparation programs serve as the bridge between academic theory and professional practice.
Educational practicums typically involve placement in schools where student teachers observe, assist, and finally lead classroom activities. The duration vary from several weeks to full semesters, depend on the program requirements and educational level. Throughout this experience, participants gradually take on increase responsibilities while receive consistent feedback from both university supervisors and cooperate teachers.
Key components of educational practicums
Observation phase
Practicums oftentimes begin with an observation period where student teachers watch experienced educators in action. During this phase, they note teaching strategies, classroom management techniques, and student engagement methods. This passive learning stage help newcomers understand the dynamics of real classrooms before take active roles.
Observation provide valuable insights into the practical application of pedagogical theories. Student teachers witness how experienced educators handle unexpected situations, adapt lesson plans to student needs, and create inclusive learning environments. This foundation prove invaluable when they begin teach.
Assisted teaching
As practicums progress, student teachers move into assist teaching roles. They might lead small group activities, help with lesson preparation, or teach portions of lessons while the corporate teacher remain present. This gradual increase in responsibility builds confidence while maintain a safety net.
During assisted teaching, practicum students receive immediate feedback on their performance. This real time guidance allow them to make adjustments and refine their approaches. The corporate teacher frequently model specific techniques beginning, so observe as the student teacher implement similar strategies.
Independent teaching
The culmination of most practicums involve periods of independent teaching where student teachers take full responsibility for classroom instruction. They plan lessons, manage student behavior, assess learn outcomes, and handle administrative tasks. This phase test their readiness for professional teaching positions.

Source: Fukuoka clinic.com
Independent teaching represent the virtually challenging and rewarding aspect of practicums. Student teachers must demonstrate their ability to apply educational theories efficaciously while respond to the unique needs of their students. Success during this phase frequently correlate with future teaching performance.
Reflection and evaluation
Throughout the practicum experience, reflection play a crucial role in professional development. Student teachers typically maintain journals, participate in debriefing sessions, and complete self assessment activities. These reflective practices encourage critical thinking about teaching methods and student outcomes.
Formal evaluations occur at regular intervals during practicums. University supervisors observe lessons, review lesson plans, and assess overall performance against established standards. These evaluations help identify strengths and areas for improvement while document professional growth.
Benefits of educational practicums
Practical skill development
Peradventure the virtually significant benefit of practicums is the development of practical teaching skills. While educational theories provide important foundations, the ability to implement these theories efficaciously require practice. Practicums offer control environments for develop essential skills like:
- Lesson planning and delivery
- Classroom management techniques
- Student assessment methods
- Differentiate instruction approaches
- Educational technology integration
- Parent and colleague communication
These skills emerge through repeat practice, constructive feedback, and guide reflection. The intensity of practicum experiences accelerate skill development beyond what classroom learns unique could achieve.
Professional identity formation
Practicums contribute importantly to the development of professional teacher identity. Through immersion in school cultures, student teachers begin to see themselves as educators instead than students. They adopt professional behaviors, ethical standards, and the specialized language of education.
This identity transformation occurs gradually as practicum students interact with experienced teachers, school administrators, and parents. They learn unwritten norms of the profession while develop their unique teaching styles. By the conclusion of successful practicums,many reportst feel li” ” real teacher” for the first time.
Reality testing
Educational practicums provide valuable reality testing for aspire teachers. The control environment allows them to confirm their career choice before full professional commitment. Some discover their passion for teach strengthens through direct experience, while others may realize they need to reconsider their career path.
This reality testing extend to preferred teaching levels and subject areas. A student who plan to teach high school mathematics might discover greater satisfaction work with elementary students. These insights prove invaluable for career planning and specialization choices.
Professional networking
Practicums facilitate important professional connections that oftentimes benefit future job searches. Student teachers meet experienced educators, administrators, and district personnel who can provide references, job leads, and mentorship. Many secure their first teaching positions through connections make during practicum experiences.
Beyond immediate employment benefits, these professional networks offer ongoing support during the challenge early years of teaching. Former cooperate teachers oftentimes remain mentors to their practicum students retentive after the formal experience conclude.
Types of educational practicums
Early field experiences
Many teacher preparation programs incorporate brief practicum experiences former in the curriculum. These introductory placements might involve limited classroom observation or assistance with specific activities. Early field experiences help students confirm their interest in teaching while connect initial coursework to real educational settings.
These experiences typically require minimal teaching responsibility but provide valuable context for subsequent education courses. Students observe diverse classroom settings and begin develop professional behaviors before more intensive practicum experiences.
Subject specific practicums
Secondary education programs frequently include subject specific practicums where students apply content knowledge in specialized settings. For example, future science teachers might complete practicums in laboratory classrooms, while music education students work with school ensembles. These specialized experiences address the unique challenges of teach particular subjects.
Subject specific practicums help bridge the gap between content expertise and pedagogical knowledge. They demonstrate how abstract concepts translate into effective instruction for specific disciplines and age groups.
Student teaching
The virtually intensive form of practicum, student teaching typically occur as a capstone experience in teacher preparation programs. These full-time placements last from one semester to a full academic year and involve progressive responsibility for all aspects of classroom instruction. Student teaching represent the final step before professional certification in most education programs.
During student teaching, participants handle the complete range of teacher responsibilities include lesson planning, assessment, parent communication, and professional development activities. University supervisors and cooperate teachers provide decrease levels of support as student teachers demonstrate readiness for independence.
Alternative certification practicums
Alternative teacher certification pathways oft include modify practicum experiences design for career changers or emergency certification candidates. These practicums might occur simultaneously with initial teaching positions, with mentors provide support while participants serve as teachers of record.
These alternative models balance the need for classroom coverage with appropriate supervision for novice teachers. While more challenging than traditional practicums, they offer important support for non-traditional pathways into education.
Challenges in educational practicums
Theory practice gap
Many student teachers report experience a” theory practice gap ” uring practicums. University coursework may present idealize teach scenarios that prove difficult to implement in real classrooms with diverse student needs and limited resources. Navigate this gap represent a significant challenge for practicum participants.
Effective practicum programs address this challenge by incorporate regular reflection sessions where students discuss the relationships between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation. University supervisors help students adapt theoretical approaches to specific classroom contexts.
Placement quality variation
The quality of practicum experiences vary substantially base on placement sites and cooperate teachers. Some student teachers benefit from exemplary mentors in advantageously resource schools, while others face less optimal conditions. This variation can affect the development of teaching skills and professional confidence.
Teacher preparation programs attempt to mitigate this challenge through careful selection of cooperate teachers and placement sites. Regular supervision helps identify problematic placements and provide additional support when needed.
Assessment complexity
Evaluate practicum performance involve complex judgments about teaching effectiveness, professional disposition, and student impact. Unlike traditional coursework with clear assessment criteria, practicums require nuanced evaluation of multifaceted skills. This complexity create challenges for both supervisors and student teachers.
Comprehensive assessment frameworks with clear rubrics help address this challenge. Regular feedback conferences allow discussion of performance indicators and progress toward professional standards.
Best practices for successful practicums
For student teachers
Successful practicum experiences require active engagement from student teachers. Effective strategies include:
- Maintain detailed reflection journals
- Seek feedback proactively
- Build relationships with all school personnel
- Observe multiple teachers beyond assign placements
- Connect regularly with university supervisors
- Participate full in school activities beyond classroom teaching
This proactive approach maximize learn opportunities and demonstrate professional commitment. Student teachers who view themselves as contribute members of school communities typically gain more from practicum experiences.
For cooperating teachers
Effective cooperate teachers balance support with appropriate challenge. They gradually release responsibility while provide constructive feedback and model reflective practice. Regular planning conferences and clear communication about expectations create optimal learning conditions.
The about effective mentors explain their decision make processes, make implicit teach knowledge explicit for novices. They create safe spaces for experimentation while maintain high standards for student learning.
For university programs
Teacher preparation programs can enhance practicum experiences through careful placement matching, comprehensive orientation for all participants, and regular communication between university and school personnel. Clear handbooks outline responsibilities and expectations help prevent misunderstandings.

Source: funlearning.ca
Progressive practicum sequences that build responsibility gradually prove more effective than isolated experiences. Integration of practicum reflections with concurrent coursework strengthen connections between theory and practice.
The future of educational practicums
Educational practicums continue to evolve to address change educational landscapes. Recent innovations include virtual practicum components allow observation of diverse classrooms beyond geographical limitations. Mixed reality simulations provide control practice environments for specific teaching challenges before real classroom implementation.
Extended residency models replace traditional student teaching with year long immersive experiences show promise results for teacher preparation. These models oftentimes include stipends or reduced tuition, make teacher preparation more accessible while provide schools with additional instructional support.
As education systems recognize the crucial importance of clinical practice in teacher preparation, practicums receive increase attention and resources. This emphasis acknowledge that effective teaching require both theoretical knowledge and extensive guide practice in authentic settings.
Conclusion
Educational practicums represent indispensable components of teacher preparation, provide the critical bridge between theoretical knowledge and professional practice. Through structured field experiences, future educators develop essential skills, form professional identities, and build networks that support career entry and ongoing growth.
Despite challenges in implementation and assessment, wellspring design practicums systematically demonstrate value for all stakeholders. Students benefit from skilled teachers whose preparation includes substantial classroom experience. Schools gain fresh perspectives and additional instructional support. Virtually significantly, practicum participants develop the practical wisdom and professional confidence necessary for effective teaching.
As education systems will continue will emphasize teacher quality as a primary factor in student success, the role of high quality practicums will potential will expand. These formative experiences remain fundamental to develop educators who can navigate the complex challenges of contemporary classrooms while meet the diverse needs of all learners.
MORE FROM oncecoupon.com